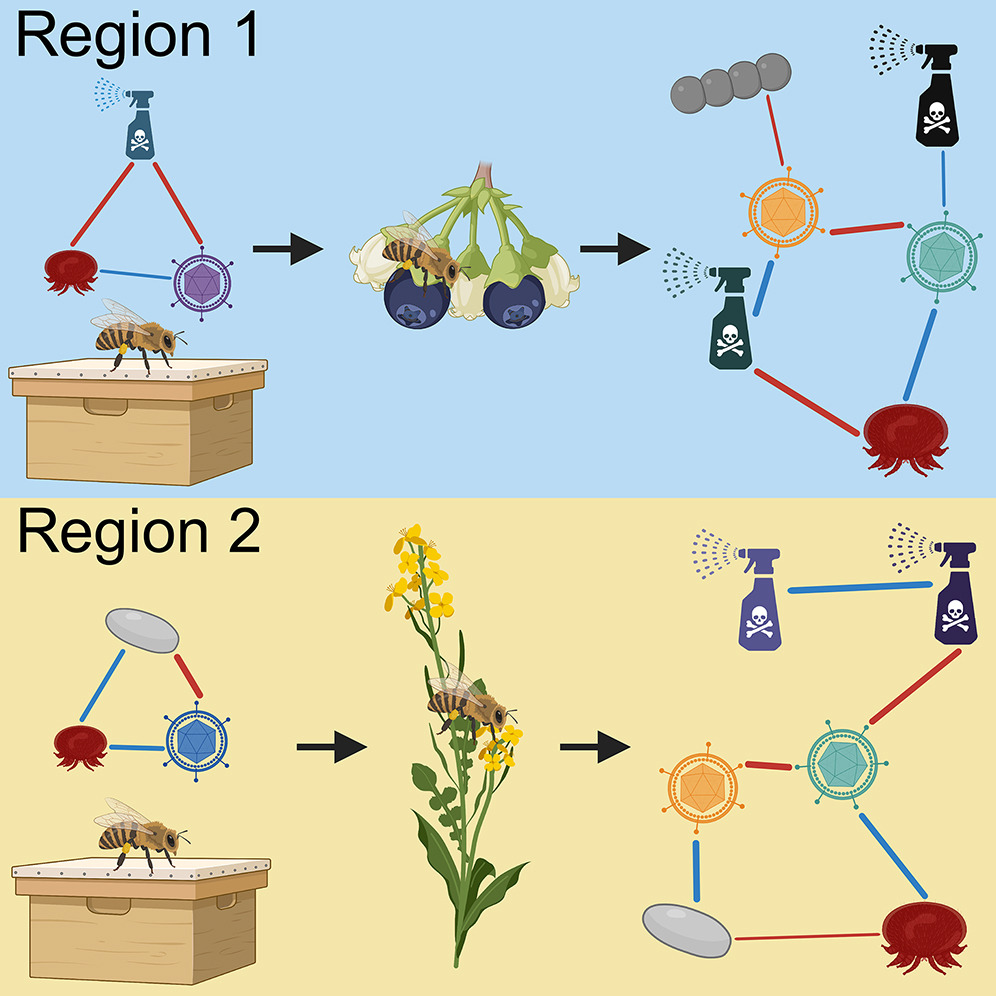
|
Bees provide a critical link in the maintenance of ecosystems through pollination. They play a major role in maintaining biodiversity, food security, nutrition, ensuring the survival of many plants, enhancing forest regeneration, providing sustainability and adaptation to climate change of agricultural production systems, and improving the quality and quantity of agricultural products.
In many rural areas of the world, beekeeping or apiculture is a widespread activity, with thousands of small-scale beekeepers depending on bees for their livelihoods. Social bees can provide humans with valuable hive products (honey, wax, propolis, pollen, royal jelly, queen bees and swarms) and services (pollination, apitherapy, apitourism and environmental monitoring) and play other important economic, cultural, and social roles.
These guidelines provide insights into the different management practices of the various social species of bees and aim to provide useful information and suggestions for making these practices more sustainable. They serve as a comprehensive guide to beekeeping for project design teams, national programme managers and policymakers wanting to improve the sustainability of beekeeping across the world and with this contributing to the FAO four betters: better production, environment, nutrition, and life.
These guidelines were produced with the support of Apimondia, the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), the Apicultural Science Association of China (ASAC) and the Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale Lazio e Toscana and many international bee experts.
|